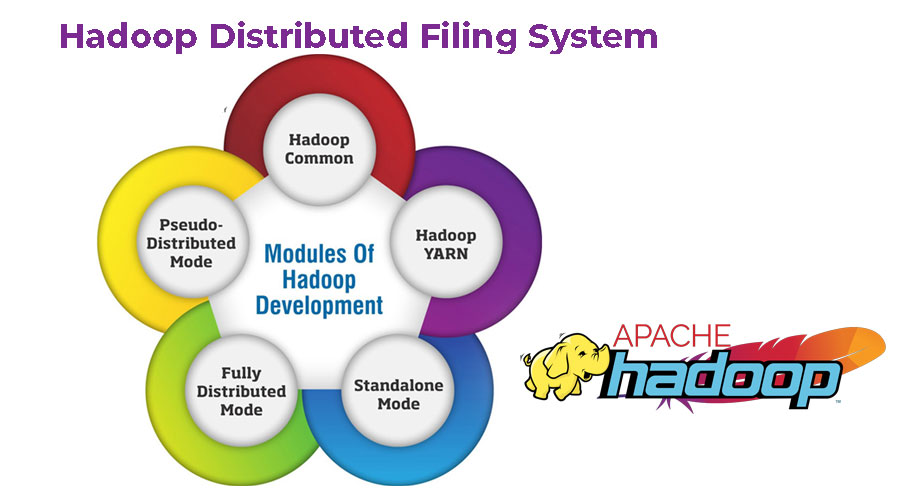
Core Components of Hadoop:
Hadoop is a framework written in Java programming language that works over the collection of commodity hardware.
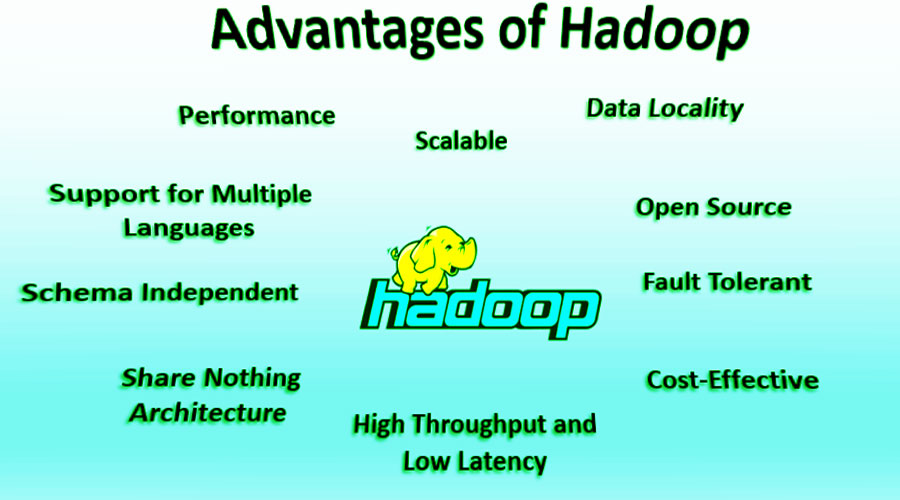
- Scalability: Hadoop can scale up from a single server to thousands of machines, handling petabytes of data.
- Cost-Effective: It utilizes commodity hardware, making it a cost-efficient solution for big data processing.
- Fault Tolerance: Data is replicated across the cluster to ensure that it remains available even if some nodes fail.
- Flexibility: Hadoop supports a variety of data formats and types, including structured and unstructured data.
To start working with Hadoop, follow these steps:
- Install Hadoop: Download and install Hadoop from the official Apache Hadoop website.
- Configure Your Cluster: Set up a Hadoop cluster by configuring the parameters for HDFS, YARN, and MapReduce.
- Run Sample Jobs: Test your setup by running sample MapReduce jobs to ensure everything is working correctly.
- Explore Hadoop Ecosystem: Familiarize yourself with related tools and frameworks such as Apache Hive, Apache HBase, and Apache Pig.
How does Hadoop work?
Hadoop allows for the distribution of datasets across a cluster of commodity hardware. Processing is performed in parallel on multiple servers simultaneously. Software clients input data into Hadoop. HDFS handles metadata and the distributed file system. MapReduce then processes and converts the data. Finally, YARN divides the jobs across the computing cluster. All Hadoop modules are designed with a fundamental assumption that hardware failures of individual machines or racks of machines are common and should be automatically handled in software by the framework.
Learn More
To deepen your knowledge of Hadoop, consider exploring these resources:
- Apache Hadoop Official Website - The primary source for Hadoop documentation and downloads.
- edX Big Data Analysis with Hadoop Course - An online course offering a comprehensive introduction to Hadoop.
- Coursera Hadoop Fundamentals - A course focused on the basics of Hadoop and its ecosystem.